Welcome to the Medical Assistant Training Manual! This comprehensive guide provides essential training materials, step-by-step procedures, and practical insights for aspiring medical assistants. Designed to cover clinical and administrative tasks, this manual ensures a well-rounded education, preparing you for real-world healthcare challenges.
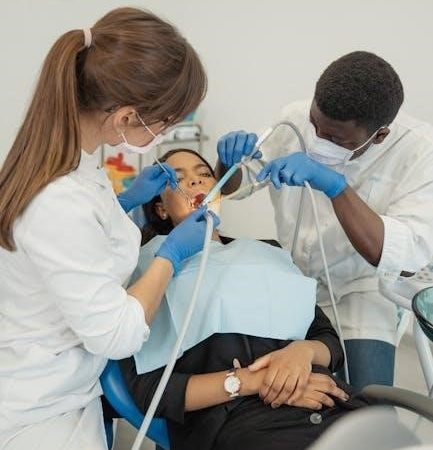
Overview of the Medical Assistant Role
A medical assistant plays a crucial role in healthcare, serving as a multi-skilled professional who bridges clinical and administrative responsibilities. They work in ambulatory care settings, assisting physicians, nurses, and other healthcare providers. Key clinical duties include patient assessment, taking vital signs, preparing patients for exams, and assisting with procedures. Administrative tasks involve managing medical records, handling billing, scheduling appointments, and ensuring HIPAA compliance. Medical assistants must possess strong communication skills, adaptability, and attention to detail to effectively support both patients and healthcare teams. This role requires a blend of technical knowledge and interpersonal skills, making medical assistants indispensable in modern healthcare delivery.
Importance of a Comprehensive Training Manual
A comprehensive training manual is essential for equipping medical assistants with the knowledge and skills needed for success. It provides clear, detailed guidance on clinical procedures, administrative tasks, and ethical considerations, ensuring consistency and clarity in training. A well-designed manual saves time, enhances learning retention, and supports ongoing professional development. It serves as a valuable resource for both new and experienced medical assistants, offering step-by-step instructions, real-world scenarios, and practical applications. By adhering to a structured format, the manual ensures that learners are well-prepared to meet the demands of the healthcare field while staying current with industry standards and best practices.
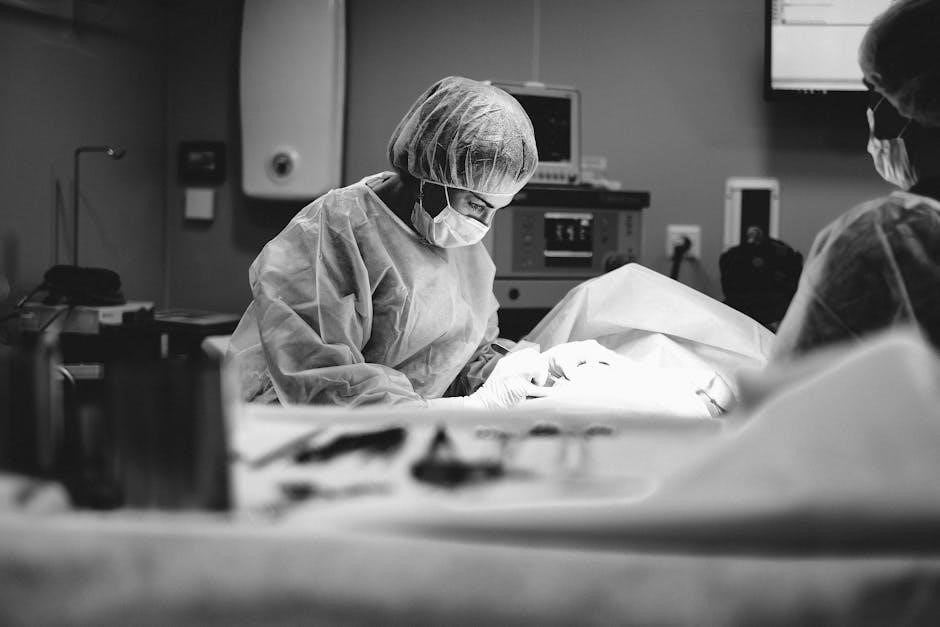
Clinical Procedures and Workflows
Clinical procedures and workflows are central to a medical assistant’s role, covering patient assessment, vital signs, infection control, and sterilization. These steps ensure efficient, safe, and high-quality care delivery.
Patient Assessment and Vital Signs
Patient assessment and vital sign measurement are fundamental skills for medical assistants. This section covers techniques for accurately measuring temperature, pulse, respiration, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation. Proper assessment ensures timely identification of abnormalities, enabling effective care. Understanding normal ranges and variations is crucial for documenting patient statuses. Additionally, visual inspections and patient histories are integral to comprehensive evaluations. Mastering these skills ensures accurate data collection, which informs clinical decisions and promotes quality patient outcomes. Regular practice and adherence to infection control protocols are emphasized to maintain safety and precision in patient care settings.
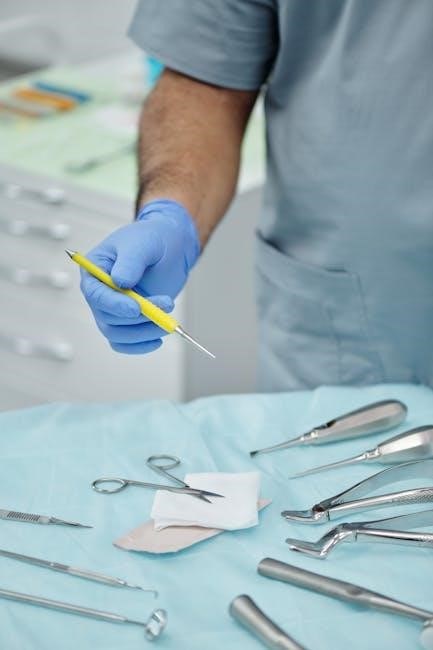
Infection Control and Sterilization Techniques
Infection control and sterilization are critical for preventing the spread of pathogens in healthcare settings. Medical assistants must adhere to strict protocols, including proper hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and surface disinfection. Sterilization techniques involve autoclaving, chemical disinfection, and ultrasonic cleaning to ensure equipment safety. Understanding the difference between cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization is vital. These practices protect both patients and staff from infections. Regular training and compliance with CDC guidelines are essential to maintain a safe environment. Proper infection control measures are integral to delivering high-quality patient care and upholding public health standards in clinical settings;
Medical Billing and Coding Essentials
Medical billing and coding are crucial administrative tasks for healthcare facilities. Accurate coding using ICD-10 and CPT codes ensures proper insurance reimbursement and data tracking. Medical assistants must understand billing processes, including patient registration, claim submission, and payment processing. Familiarity with EHR systems streamlines documentation and reduces errors. Compliance with HIPAA regulations is essential to protect patient privacy. Proper coding and billing practices prevent financial discrepancies and legal issues. Training in medical billing and coding equips assistants with the skills to manage healthcare finances efficiently, ensuring seamless operations in clinical settings. This expertise is vital for maintaining accurate records and fostering trust between patients and healthcare providers.

Administrative Tasks and Responsibilities
Medical assistants handle scheduling, office management, and patient records. They ensure efficient workflow, maintain compliance with regulations, and support healthcare providers in delivering quality care. Accuracy is key.
Office Management and Scheduling
Effective office management and scheduling are critical skills for medical assistants. This includes managing patient appointments, maintaining accurate records, and ensuring smooth office operations. Key responsibilities involve coordinating schedules, handling patient flow, and utilizing electronic health records (EHR) systems for efficient data management. Medical assistants must also manage front-desk duties, such as check-in/check-out processes, insurance verification, and billing tasks. Strong organizational and communication skills are essential to ensure seamless coordination between patients, providers, and administrative staff. Proper scheduling and office management contribute to a positive patient experience and support the overall efficiency of healthcare facilities. These tasks require attention to detail and adherence to compliance standards.

Electronic Health Records (EHR) Management
Electronic Health Records (EHR) management is a cornerstone of modern healthcare administration. Medical assistants play a vital role in maintaining accurate and secure patient records within EHR systems. Key responsibilities include documenting patient histories, medications, lab results, and treatment plans. Proper data entry ensures continuity of care and reduces errors. Medical assistants must also comply with HIPAA regulations to protect patient confidentiality. Proficiency in EHR systems, such as eClinicalWorks (eCW), is essential for efficient patient care and office operations. Regular updates and accurate documentation are critical to maintaining reliable records. Effective EHR management enhances patient care, streamlines workflows, and supports healthcare providers in making informed decisions.
Communication Skills for Patient Interaction
Effective communication is crucial for medical assistants to build trust and ensure clear interactions with patients. Key skills include active listening, empathy, and clarity when explaining procedures or instructions. Medical assistants must adapt their communication style to meet the needs of diverse patients, including those with emotional or language barriers. Maintaining a professional and compassionate tone helps alleviate patient anxiety. Additionally, clear and concise documentation of patient interactions is essential for accurate record-keeping. Strong communication fosters a positive patient-provider relationship, enhances care quality, and ensures that patient concerns are addressed promptly and appropriately. These skills are vital for providing exceptional patient care in any healthcare setting.

Ethical Considerations and Professionalism
Medical assistants must uphold professionalism and adhere to ethical standards, ensuring respect, confidentiality, and honesty in all patient interactions. Demonstrating integrity and accountability is essential for building trust and maintaining high-quality care.
HIPAA Compliance and Patient Confidentiality
HIPAA compliance is a cornerstone of medical assistant training, ensuring the protection of patient health information (PHI). Medical assistants must adhere to strict guidelines to maintain confidentiality, including securing electronic records and avoiding unauthorized disclosure. Proper handling of PHI involves limiting access to only necessary personnel and using secure methods for transmitting patient data. Violations of HIPAA can result in severe legal consequences. Training emphasizes understanding privacy rights, recognizing potential breaches, and reporting incidents promptly. By upholding HIPAA standards, medical assistants build trust with patients and contribute to ethical healthcare practices. This section outlines essential protocols for safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring compliance in daily operations.
Scope of Practice and Delegation
Understanding the scope of practice is crucial for medical assistants to perform tasks within legal and professional boundaries. This includes both clinical and administrative duties, varying by state and employer. Delegation involves transferring tasks from healthcare providers to medical assistants, ensuring they remain within their competency. Proper delegation enhances teamwork, patient care, and operational efficiency. Medical assistants must avoid exceeding their scope, as it can lead to legal or ethical issues. Clear communication and respect for professional boundaries are essential. This section outlines guidelines for understanding responsibilities, accepting delegated tasks, and maintaining accountability to ensure high-quality, safe patient care while respecting legal and ethical standards in healthcare settings.
Professional Behavior in Healthcare Settings
Professional behavior is fundamental for medical assistants to maintain a respectful and efficient healthcare environment. This includes adhering to ethical standards, demonstrating empathy, and ensuring patient confidentiality. Clear communication with both patients and colleagues fosters trust and collaboration. Maintaining a neat appearance, punctuality, and a positive attitude are essential. Proper etiquette in documentation and electronic health records ensures accuracy and compliance. Respecting diversity and cultural differences among patients and staff promotes inclusivity. Continuous learning and self-improvement are expected. By upholding these professional standards, medical assistants contribute to a positive workplace culture and deliver high-quality patient care while maintaining the integrity of the healthcare team and organization.

Practical Applications and Hands-On Training
This section focuses on applying theoretical knowledge through real-world case studies, preceptorship programs, and mentorship. Hands-on training enhances clinical and administrative skills, preparing students for practical challenges in healthcare settings.
Case Studies and Real-World Scenarios
Case studies and real-world scenarios are integral to medical assistant training, bridging theory and practice. These exercises simulate patient interactions, enabling trainees to apply knowledge in realistic clinical and administrative contexts. By analyzing scenarios, such as documenting vital signs or preparing for emergencies, students develop critical thinking and decision-making skills. Practical examples, like assisting with debridement or managing patient charts, enhance proficiency in diverse healthcare settings. These tools foster confidence and readiness to handle actual patient care situations effectively, ensuring a smooth transition from training to professional practice.
Preceptorship and Mentorship Programs
Preceptorship and mentorship programs are vital for medical assistant training, offering hands-on experience and professional guidance. These programs pair trainees with experienced healthcare professionals who provide one-on-one support, helping them navigate clinical and administrative responsibilities. Preceptors assist with orientation, skill development, and workflow familiarization, while mentors offer career advice and industry insights. Such programs ensure a smooth transition from education to practice, fostering confidence and competence; They also encourage continuous learning and professional growth, equipping medical assistants with the tools to excel in diverse healthcare settings and adapt to evolving industry standards.